This guide helps you to install and configure the latest WordPress on an Ubuntu Server. It covers Apache, MariaDB, PHP, and WordPress configurations.
Steps
- Installation and configuration of Apache2
- Installation and configuration of MariaDB
- Installation and configuration of PHP and Apache modules
- Create WordPress database and user
- Setup and configure WordPress
- Configure Apache For WordPress
- Accessing the WordPress dashboard
Installation and configuration of Apache2
Step 1: Login to the server and update the package repos.
sudo apt-get update -yStep 2: Install Apache2
sudo apt-get install apache2 -yStep 3: Disable anonymous directory listing.
sudo sed -i "s/Options Indexes FollowSymLinks/Options FollowSymLinks/" /etc/apache2/apache2.confStep 4: Start, enable, and check the status of Apache2
sudo systemctl stop apache2
sudo systemctl enable apache2
sudo systemctl start apache2Installation and configuration of MariaDB
Step 1: Install the MariaDB database server and client
sudo apt-get install mariadb-server mariadb-client -yStep 2: Use the following commands to start, stop, enable, and check the status of the MariaDB service.
sudo systemctl stop mysql
sudo systemctl enable mysql
sudo systemctl start mysql
sudo systemctl status mysqlStep 3: Setup the root admin password for the database using mysql_secure_installation command. It will prompt you to set up the new password.
sudo mysql_secure_installationUse the following options for the prompt.
Enter current password for root (enter for none):
Switch to unix_socket authentication [Y/n]: Y
Change the root password? [Y/n]: Y
New password: <Enter new password for MariaDB root>
Re-enter new password: <Repeat password>
Remove anonymous users? [Y/n]: Y
Disallow root login remotely? [Y/n]: Y
Remove test database and access to it? [Y/n]: Y
Reload privilege tables now? [Y/n]: Y Step 4: Restart the database server for the changes to take effect.
sudo systemctl restart mysqlInstallation and configuration of PHP and Apache modules
Step 1: Install latest PHP and its related modules.
sudo apt install -y php php-mysql php-cli php-cgi php-gd libapache2-mod-phpStep 2: Open /etc/php/8.3/apache2/php.ini file
sudo vi /etc/php/8.3/apache2/php.iniAdd the following contents to the file. List of supported timezones: https://www.php.net/manual/en/timezones.php
file_uploads = On
allow_url_fopen = On
memory_limit = 256M
upload_max_filesize = 150M
max_execution_time = 350
date.timezone = UTCCreate WordPress Database and user
Step 1: Login to the database using the password you set for root.
sudo mysql -u root -pStep 2: Create a database named “wp-db”
CREATE DATABASE wp-db;Step 3: Create a new database user named “wpadmin” and set a custom password. This user will be used in the WordPress configuration.
CREATE USER 'wpadmin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your_password_here';Step 4: Grant all privileged on wordpress-db for wordpress-admin user. Replace the password you set for wordpress-admin.
GRANT ALL ON wp-db.* TO 'wpadmin'@'localhost' IDENTIFIED BY 'your-password-here' WITH GRANT OPTION;Step 5: Flush all privileges and exit the db shell.
FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
exitSetup and configure WordPress
Step 1: Download the latest WordPress
wget https://wordpress.org/latest.tar.gzStep 2: Untar the WordPress files
tar -xvf latest.tar.gzStep 3: Move the WordPress folder to /var/www/html folder.
sudo mv wordpress /var/www/html/wordpressStep 4: Change the ownership of the wordpress folder to www-data
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /var/www/html/wordpress/Step 5: Change the folder and file permissions using the following command. Folders should have 755 permission, and files should have 644 permission.
find /var/www/html/ -type d -print0 | xargs -0 chmod 0755
find /var/www/html/ -type f -print0 | xargs -0 chmod 0644Step 6: Remove the downloaded wordpress installation file.
rm latest.tar.gzYou can check if the permissions have been applied using the following command.
stat -c "%a %n" /var/www/html/wordpress/*Configure Apache For WordPress
Step 1: Create a new Apache configuration named wp-site.conf for the WordPress site.
sudo vi /etc/apache2/sites-available/wp-site.confAdd the following configuration to the file and save it. Replace yourdomain with your custom domain name.
<VirtualHost *:80>
ServerAdmin admin@yourdomain.com
DocumentRoot /var/www/html/wordpress/
ServerName yourdomain.com
ServerAlias www.yourdomain.com
<Directory /var/www/html/wordpress/>
Options +FollowSymlinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>
ErrorLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/error.log
CustomLog ${APACHE_LOG_DIR}/access.log combined
</VirtualHost>Step 2: Enable wp-site.conf
sudo a2ensite wp-site.confStep 3: Enable the Apache rewrite module.
sudo a2enmod rewriteStep 4: Restart the Apache server.
sudo systemctl restart apache2Configure WordPress Application
Step 1: Rename the default wp-config-sample.php to wp-config.php
sudo mv /var/www/html/wordpress/wp-config-sample.php /var/www/html/wordpress/wp-config.phpStep 2: Open the wp-config.php file
sudo vi /var/www/html/wordpress/wp-config.phpReplace the values highlighted in the image below with the database, user, and password generated in the previous steps.
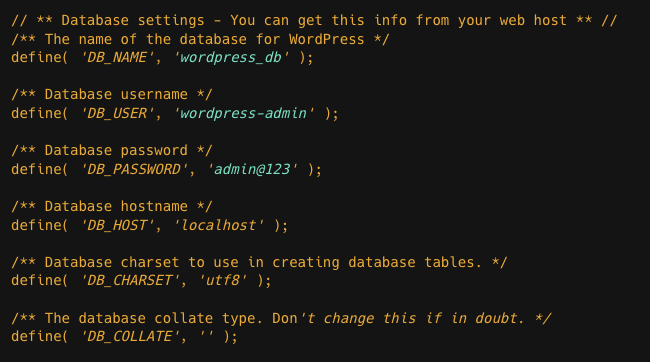
Step 3: Now you have configured your site details on the wp-site.conf file, try to access WordPress by browsing the domain name you used on the wp-site.conf file.
Make sure your server is mapped to the domain name you configured in the wp-site.conf file.
http://your-domain-name.comIf you haven’t configured a domain name, you can access the installed WordPress with
http://<your-server-ip>/wordpress Step 4: Select the preferred language and fill up the details in the configuration wizard.
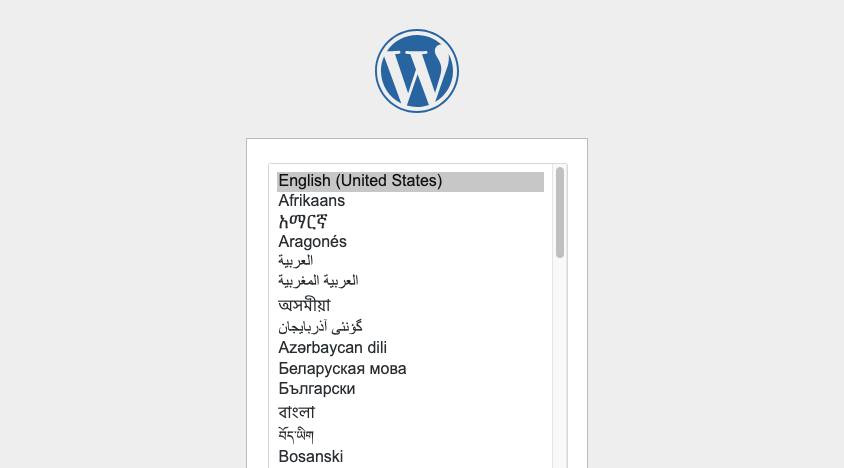
Step 5: Once WordPress is installed, you can access the dashboard using the username and password.